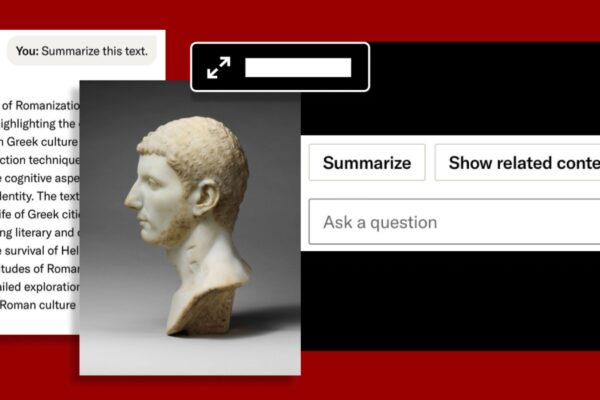
AI research tool
Get to know our AI research tool, part of a growing suite of AI-enabled features on JSTOR designed to enhance—not replace—the research process.
Developed in collaboration with our community and offered free to JSTOR-participating institutions, the tool helps users engage more deeply with JSTOR’s trusted corpus.
Have questions, comments, or concerns? We want to hear from you!

About the tool
Our AI research tool appears on content pages for journal articles, book chapters, research reports, and in search workflows that go beyond standard keyword matching to help you:
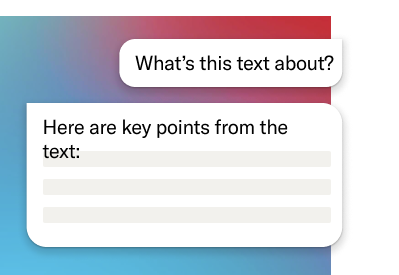
Assess content relevance
Quickly decide whether a text is relevant to your research by surfacing key points and arguments.

Deepen your research
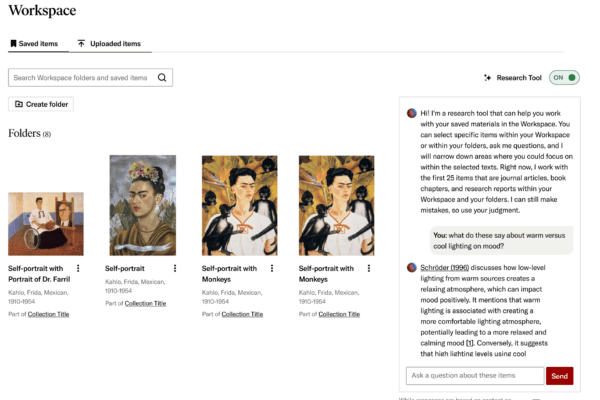
Discover related topics and materials across the JSTOR corpus.
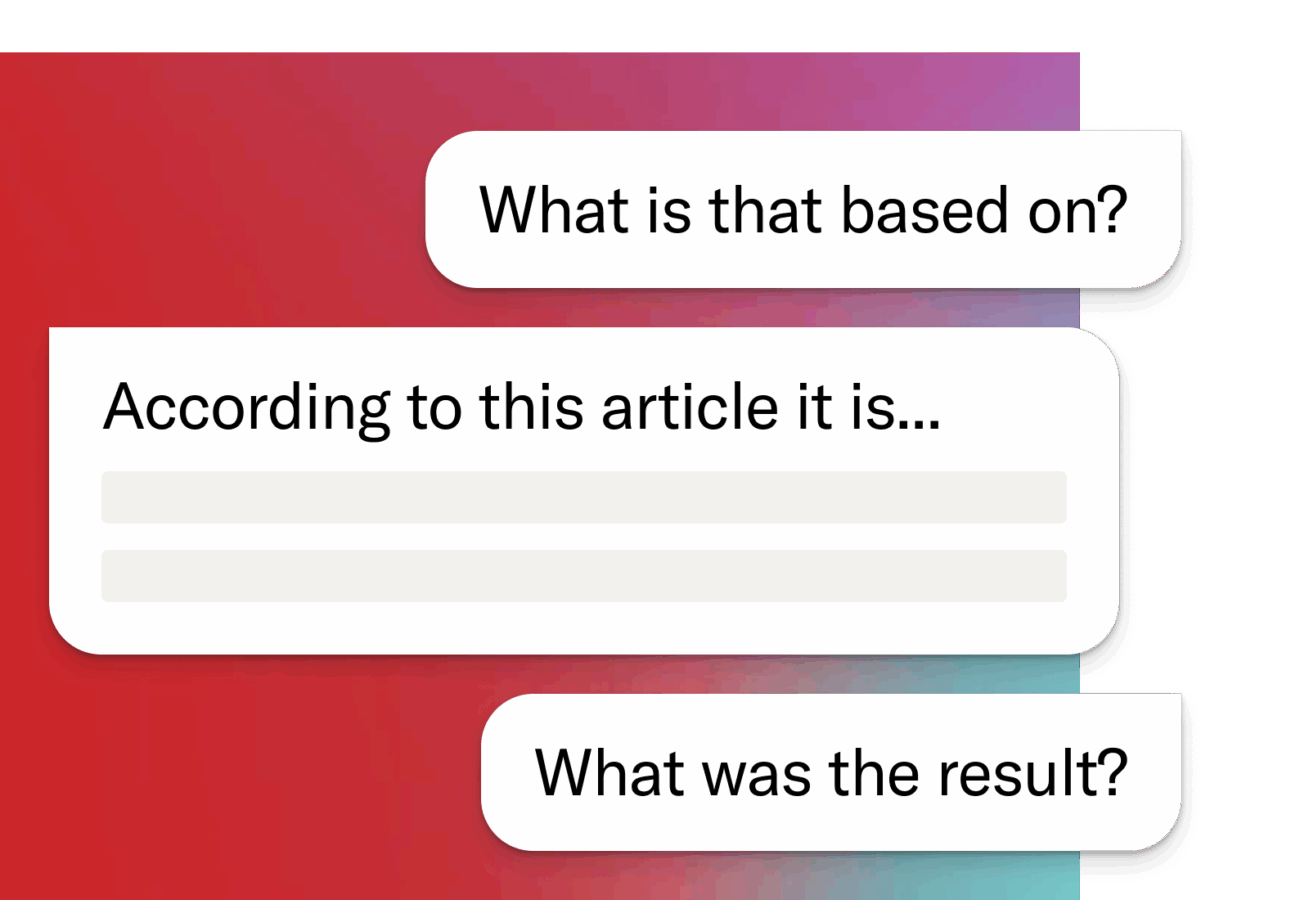
Be conversational
Use natural language to search JSTOR, or ask questions about what you’re reading.
Community voices
The AI research tool in action
Frequently asked questions
What does the tool do?
Our research tool leverages AI to help users:
- Identify relevant material faster by surfacing key points and arguments from full-text documents
- Discover new topics and content exclusively within the JSTOR corpus
- Be conversational by using natural language to ask questions about the text being viewed, or search JSTOR in a new way
By using the tool and sharing your feedback, you can help us continue to refine its capabilities.
What types of content does the tool support?
At present, the tool works with journal articles, book chapters, and research reports on JSTOR. It does not yet support images, audio, video, and text-based primary sources.
What data sources is the tool drawing from to generate responses?
To start, we are using only the contents of the document being viewed to generate responses. Over time, as we learn from and improve upon the accuracy of responses, we might extend this to use the content of other relevant items within (but not beyond) the JSTOR corpus.
Which large language models (LLMs) are JSTOR using?
We currently use GPT-4o mini and GPT-4.1 nano from OpenAI, plus the open-source all-MiniLM-L6-v2 sentence transformer model. We continue to evaluate newer models to determine which ones best fit our use cases as our needs evolve.
How do you measure or ensure accuracy?
We monitor and continuously improve accuracy through:
- Subject matter expert review of tool outputs
- User feedback gathered via in-tool responses and ongoing qualitative research with students, faculty, and librarians
- Model performance evaluation for our specific use cases using industry-standard metrics for Machine Learning (ML) and Natural Language Processing (NLP). Additionally, we continuously integrate new evaluation metrics specifically developed for Large Language Model (LLM) use cases.
How will my information be kept, shared, and/or used?
JSTOR handles all personal information, including information provided to the tool, in accordance with our privacy policy. JSTOR does not sell user data, nor does it share content or user data from its platform for the purposes of training third-party large language models (LLMs). For more information about JSTOR’s privacy practices and the practices of the LLMs used by the tool, see “Data collection and use” in the Legal notices section of this page.
Why do I have to log into a personal account to access JSTOR’s AI-enabled features?
Accessing JSTOR’s AI-enabled features requires a personal account to support transparency and shared accountability for how the tool is used. Logging in helps JSTOR manage user permissions effectively, safeguarding user data and privacy while allowing for tailored access based on institutional affiliations and user preferences. This approach helps balance transparency, academic integrity, and user support.
What is JSTOR doing to offset the environmental impacts of AI?
We recognize the environmental impact of AI and closely follow emerging research in this area. Our approach prioritizes making informed, responsible choices that minimize our footprint while supporting our commitment to advancing research and learning through new technologies. Wherever possible, we prioritize thoughtful implementation over scale for scale’s sake. Here are some of the ways we reduce our impact:
- We don’t train our own LLMs. Model training is resource-intensive, so we rely on existing models and focus on using them efficiently.
- We choose the right model for the task. Rather than defaulting to the largest model, we select the most appropriate option, using smaller models when possible to reduce energy use while maintaining quality.
- We cache repeatable responses. For example, if a user asks “What is this text about?” on an article without an abstract, the LLM generates a response just once. Future users who ask this question on the same article will see the same response without triggering a new LLM request. That will be the same for each user, like summaries.
- We keep prompts lean. We craft our system prompts to be as concise as possible while still providing the necessary context to ensure high-quality results. Smaller inputs mean less computational overhead.
Will there be fees associated with the tool?
No. The tool is offered at no additional cost to JSTOR-participating institutions as part of our nonprofit commitment to equitable access.
What kind of control do institutions and individuals have?
We recognize that institutions and individuals vary in their approach to AI.
- For JSTOR-participating institutions, the tool is enabled by default, but JSTOR administrators can disable or re-enable it at any time via the Admin portal. Learn more.
- Individual users can also turn off the tool within their own interface by toggling visibility on JSTOR item pages.
If the tool is disabled for an institution, users will not see the option to use it. Please note that if a user has access to JSTOR through multiple institutions, they may still retain access to the tool through another institution.
Is my institution eligible for access to the tool?
If your institution participates in JSTOR, you should have access to the tool as of late July 2025. If you’re unsure, please contact support. If your institution has access to JSTOR, and the tool is not visible to you, your JSTOR account administrator may have disabled these features.
How is content protected from unauthorized or malicious use?
JSTOR maintains physical, technical, and administrative safeguards to protect the content we hold. We are a SOC2 compliant organization whose data security practices and measures are audited annually by independent third parties.
Content is only processed internally and with the OpenAI API. Please note that OpenAI API only temporarily stores data for processing purposes and does not use the submitted data to train their models or enhance their services. For more information on OpenAI’s data security practices, please consult the OpenAI Trust Portal and Amazon Bedrock policy.
What is JSTOR’s overall approach to AI and other emerging technologies?
Technology has always been an incredible accelerator for ITHAKA’s mission to improve access to knowledge and education. Since launching a limited beta of the AI research tool in August 2023, JSTOR has worked with thousands of community members, including librarians, faculty, and students, to ensure that AI and other advanced technologies are applied responsibly and meaningfully on the platform.
Guided by feedback from over 150,000 users in more than 160 countries—as well as robust user research, expert testing, and ongoing monitoring—we’ve developed a scalable, academically grounded tool designed to support real-world research needs.
As a trusted provider of scholarly materials, we have a responsibility to leverage content, technology, and deep subject matter expertise to chart a path forward that makes the use of AI safe, effective, and affordable for our constituents. Our approach is rooted in the following principles:
- We honor our values first and foremost. JSTOR provides users with a credible, scholarly research and learning experience. Our use of technology must enhance that credibility, not undermine it.
- We listen closely and proceed with care. We recognize the concerns associated with AI and other emerging technologies and pursue this work in close collaboration with our community.
- We empower people, not replace them. These tools should not be used to “do the work.” They are designed to help people deepen and expand their work.
- We enable our systems to interact with users in ways that are intuitive. Traditionally, it has been the users’ responsibility to adapt to restricted language and structures to provide computers with inputs. Today, computers can interact effectively with users in natural language, and we should take advantage of that, while balancing the need to support user and institutional preferences.
This work is ongoing. As we learn and grow, we welcome your engagement to help shape AI tools that reflect shared values and advance meaningful access to scholarship.
Promote the tool at your institution
Build awareness of, and engagement with, JSTOR’s AI research tool at your institution with these ready-made resources. From training materials and social media posts to customizable web copy, our toolkit has everything you need to help your community get the most out of this innovative tool.

Exploring new technologies at ITHAKA
ITHAKA offers a portfolio of nonprofit services, including JSTOR, Portico, and JSTOR Digital Stewardship Services, aligned around a shared mission to improve global access to knowledge as affordably and sustainably as possible. Technology is central to achieving this goal. Through Ithaka S+R’s research and ongoing enhancements to JSTOR’s research and learning tools, we are actively exploring the use of AI and other emerging technologies to advance education and scholarship.
Advancing digital stewardship
Part of JSTOR Digital Stewardship Services, JSTOR Seeklight is our AI-powered technology that enhances digital collections processing workflows, drawing on JSTOR’s infrastructure and engineering, along with deep community expertise.
Generative AI and higher education
Ithaka S+R is working to uncover the implications of generative AI for higher education and discover its potential to support instructors, students, and researchers.
Sharing insights and learnings
We’re continuously sharing insights from real-world applications, usage, and user feedback. Stay updated on our latest findings on our blog.
Legal notices
Please keep the following in mind as you explore AI on JSTOR.
By using JSTOR’s AI research tool, you consent to JSTOR collecting any data that you choose to share with the tool. JSTOR retains your conversation history in our logs and uses it in de-identified form, in accordance with our privacy policy, to maintain and improve the tool. We won’t ask you for any personal information, and request that you not share any in your conversations.
Any data sent to large language models (LLM) providers (which includes your prompt and some or all of the text of the content being viewed) is used only for generating the response. They do not use this to further train their models, nor do they retain the data for more than 30 days, in accordance with OpenAI’s API data usage policies.
Use of the tool is subject to the JSTOR Terms and Conditions of Use. In particular, users should be aware of Section 7d describing the operation and limitation of the tool. Please note that current user experience may vary and may not be reflective of the tool’s future capabilities.
Feedback
Any suggestions, ideas, or other information you would like to share regarding the tool may be used to improve, enhance, or develop its features. By submitting user feedback, you agree that such feedback becomes the sole property of JSTOR, and waive any rights, including intellectual property rights, related to the feedback.
View image credits from this page

Odra Noel. Origin of Life. n.d. Part of Open: Wellcome Collection, Artstor.

Vincent van Gogh. Apples. n.d. Part of Erich Lessing Culture and Fine Arts Archives, Artstor.